Tachycardia (Rapid Heartbeat)
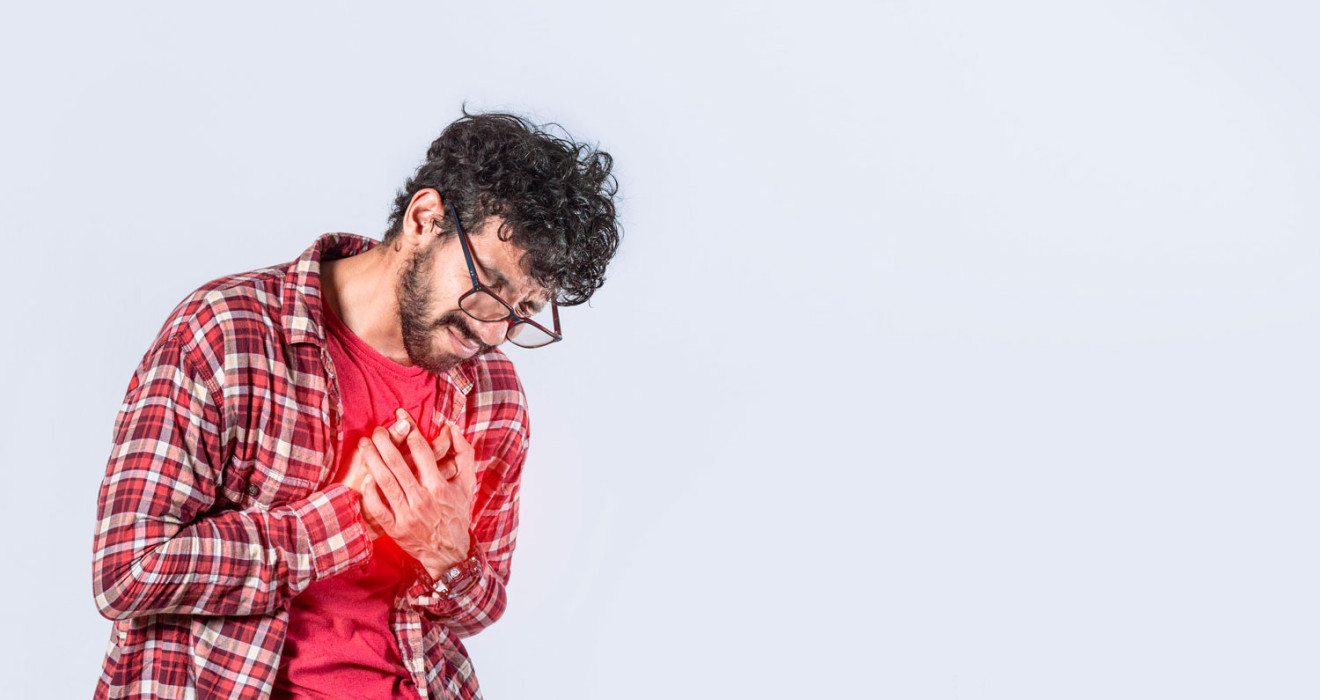
Tachycardia is the condition characterized by the heart beating faster than normal. In a healthy adult, the resting heart rate should range between 60 and 100 beats per minute. However, in cases of it, the heart rate exceeds these limits. There are various causes and types of it.
What is Tachycardia?
It is a condition where the heart beats faster than the normal range. In a healthy adult, the resting heart rate should be between 60 and 100 beats per minute. In cases of rapid heartbeat, the heart rate goes above 100 beats per minute.
What are the Types of It?
Some common types of tachycardia include the following:
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): It occurs due to rapid and irregular contractions of the atria.
- Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): It occurs due to rapid and irregular contractions of the ventricles.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AF): It results from the irregular and rapid trembling of the atria.
- Sinus Tachycardia: It refers to the condition where the heart rate originating from the sinus node exceeds 100 beats per minute.
What Causes Tachycardia?
It can occur due to various factors, including:
- Stress or anxiety
- Physical activity or exercise
- High fever
- Electrolyte imbalances (such as potassium or sodium)
- Thyroid problems
- Heart diseases (such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, etc.)
- Side effects of medications
- Consumption of caffeine or stimulant drugs
- Alcohol or drug use
- Anemia and iron deficiency
What are the Tachycardia Symptoms?
Some common symptoms of tachycardia include:
- Rapid and irregular heartbeats
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Dizziness or fainting sensation
- Fatigue or weakness
- Headaches
- Sensation of palpitations
- Sweating
How is it Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of rapid heartbeat is made through an evaluation and tests conducted by a doctor. Doctor will listen to your symptoms, take your medical history, and perform a physical examination. The following tests may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause of tachycardia:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Holter monitoring
- Echocardiography (Cardiac ultrasound)
- Exercise stress test
- Electrophysiological study (EPS)
What are the Complications of Tachycardia?
When left untreated or uncontrolled, rapid heartbeat can lead to serious complications, including:
- Heart failure
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Loss of consciousness
- Sudden death
What are the Tachycardia Treatment Options?
The treatment of tachycardia varies depending on the underlying cause. The treatment options include:
- Medications: Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmic drugs, and other medications can be used to regulate heart rhythm and control episodes.
- Electrophysiological Ablation: In this procedure, a catheter is used to eliminate abnormal rhythm in the heart.
- Pacemaker: In certain types of it, a pacemaker can be used to restore regular heartbeats and maintain a normal rhythm.
- Cardioversion: It is a procedure that aims to correct the heart's rhythm using an electrical shock.
- Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle modifications such as stress management, regular exercise, healthy eating, and limiting tobacco or alcohol consumption can help control the symptoms of it and prevent recurrence.
- If it is secondary to an underlying cause, treating the root cause may be necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
To prevent it, you can follow the steps below:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Take medications regularly.
- Maintain electrolyte balance.
- Avoid stress.
-
All types of tachycardia have the potential to be serious. However, some are more dangerous and may require urgent medical intervention. Particularly, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, which are ventricular-focused tachycardia types, are considered dangerous as they can lead to cardiac arrest and life-threatening risks.
-
Psychogenic heart palpitations refer to the awareness of transient, rapid, or irregular heartbeats that occur due to emotional or psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, fear, or excitement. In this condition, the heart may beat faster or irregularly than normal. Psychogenic heart palpitations are generally temporary and harmless, although the symptoms can be distressing.
-
It attack refers to a situation where the symptoms of it manifest intensely.
-
In a healthy adult at rest, the pulse rate generally falls between 60 and 100 beats per minute. However, a pulse rate exceeding 100 beats per minute at rest is considered as a rapid heartbeat or tachycardia.