Radial Angiography (Wrist Angiography)
Angiography is a procedure a cardiologist performs in a hospital or medical centre. It is usually performed under local anaesthesia. Sedation can also prevent the patient from feeling pain or discomfort. During angiography, a catheter or tube is generally placed in the femoral artery in the groin area or the artery in the wrist (radial angiography). The image is taken with an X-ray device by injecting contrast material.
What is Angiography? Which Body Parts Are Suitable For The Procedure?
Angiography is the medical procedure used to take X-ray images of blood vessels. During this procedure, a doctor inserts a thin catheter or tube into an artery and injects contrast material to take X-ray images of the blood vessels.
It is generally used to image vessels in different body parts, such as coronary, cerebral, renal, leg, and carotid arteries. In this way, it has an important place in diagnosing and treating diseases. For example, it can be used to diagnose or treat conditions such as heart attack, coronary artery disease, cerebral haemorrhage or stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
What is Radial Angiography (Wrist Angiography)?
Radial or wrist angiography is an imaging method to look at the heart and vascular system through a thin catheter inserted into a person's wrist. It is also known as arm angiography.
Radial angiography allows the patient to recover faster than femoral angiography. It also causes fewer complications.
It is preferred, especially in younger patients with difficulty accessing the femoral artery. However, in some cases, some patients are not suitable for this procedure. Therefore, the physicians should determine the most appropriate angiography method for each patient according to the patient's characteristics and condition.
How is It Performed?
Wrist angiography includes the following steps:
- Preparation of the patient: The patient must first be fasting. Usually, at least 6 hours should pass after the last meal. During angiography, local anaesthesia is applied for the comfort of the patient.
- Access to the radial artery: The radial artery in the wrist is anaesthetized with local anaesthesia, and a thin catheter is inserted.
- Contrast material injection: Contrast material is injected into the artery through the catheter and is used to take X-ray images. The contrast medium provides detailed pictures that show stenosis, occlusion, or other abnormalities in the arteries.
- X-ray: After injecting the contrast agent, the cardiologist uses the X-ray device to take an image of the arteries and the heart. These images are used to evaluate the cardiovascular system and detect abnormalities.
- Catheter removal: After the wrist angiography, the catheter is carefully removed, and a compression band is applied. This pressure must be held firmly for several hours to stop the bleeding and help the artery to heal.
Which Patients Are Suitable for Wrist Angiography?
It is preferred, especially in young patients and patients who have difficulty accessing the femoral artery. It can also be preferred for patients who experience complications with previous femoral angiography.
What are the Advantages of Radial Angiography?
It has many advantages over other angiography methods. These advantages are as follows:
- It carries less risk of bleeding than femoral angiography. Because the artery in the wrist is smaller, the risk of bleeding is lower.
- Patients usually have shorter hospital stays.
- Since the artery in the wrist is smaller, the healing process is faster. There is also usually less pain and discomfort after the procedure.
- Wrist angiography reduces the risk of infection because the artery in the wrist is easier to clean.
Who Is not Eligible for Wrist Angiography?
It can be used safely and effectively in most patients. However, in some cases, it is not an appropriate procedure for patients. These situations are as follows:
- Occlusion or narrowing of the radial artery
- Allergy
- Infection or inflammation of the arteries in the wrist
- Blood clot or bleeding disorder
- Thin or weak arteries in the wrist
- Pregnancy
What is the Healing Process After Radial Angiography?
The healing process is lighter than other angiography procedures. After the procedure, you can be discharged to your home or hospital's short-term hospitalization units at the end of the same day. However, the healing process varies from person to person.
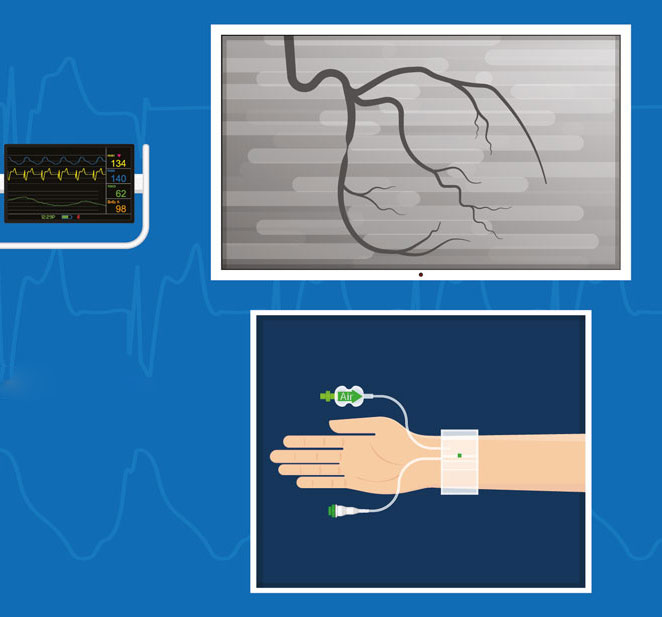
How is the Process After Radial Angiography?
It would help if you protected the band or bandage on your wrist for the first few hours after the procedure. This tape or dressing is tightly wrapped to help stop bleeding and is usually removed after 2-4 hours.
There may be swelling, pain, or mild bruising in the wrist. These symptoms usually go away on their own. However, you may need to take mild pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs for a few days after the procedure. Your doctor will tell you which drugs are suitable for you.
It is crucial to avoid heavy exercise, heavy lifting and driving for 24 hours after the procedure. Light activities can be done for a few days.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
It takes approximately 20-30 minutes. However, when the preparation and recovery periods are added before and after the procedure, the total time is about 1-2 hours.
-
As with any invasive procedure, it has risks. Risks include bleeding, infection, vessel damage, heart attack and stroke. However, these risks are infrequent.
-
Yes, it can be performed on both arms. However, the procedure is usually performed on the right arm.
-
Doctors usually insert a stent if vascular occlusion is detected during the angiography procedure.
-
It can be repeated as long as necessary. However, your doctor will decide if it is required to repeat the procedure.

