Carotid Artery Occlusion (Carotid Stenosis)
Carotid artery occlusion is a condition caused by narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries in the neck. This can result in insufficient blood supply to the brain, which can affect brain function. It is usually progressive and can have serious consequences if not diagnosed early.
What is Carotid Artery Occlusion?
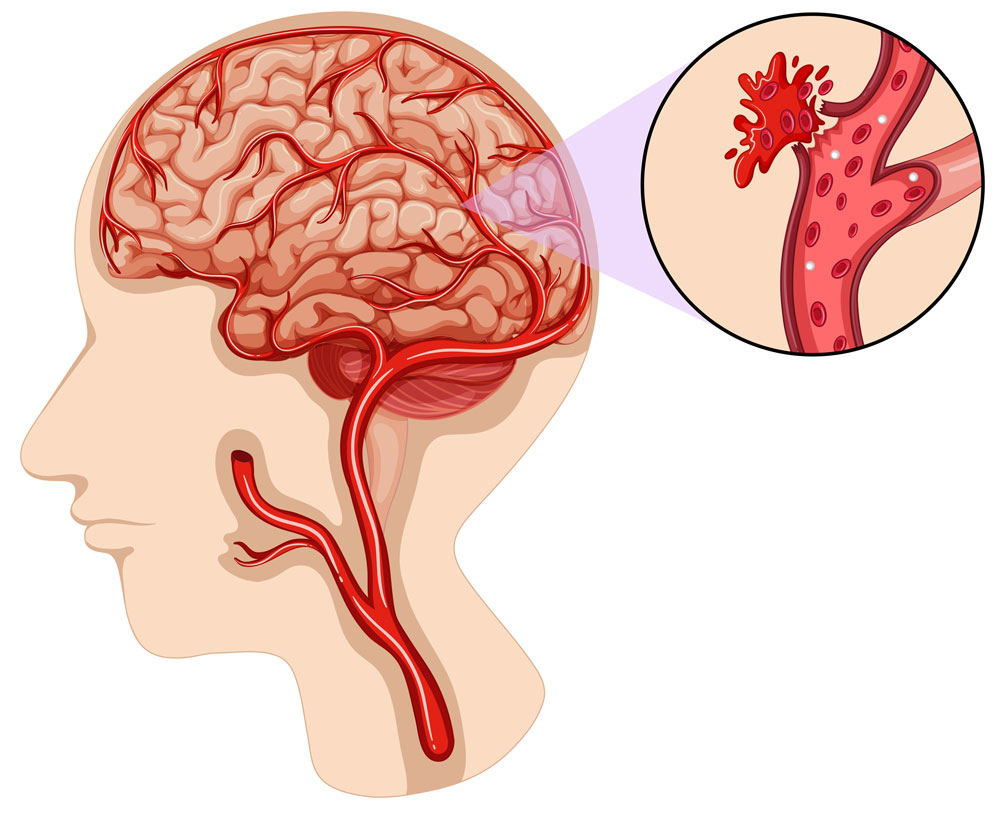
Carotid stenosis is a blockage or narrowing of the carotid artery, one of the main vessels that carries blood to the brain and face. This condition can cause serious health problems by affecting blood flow to the brain and face.
Why Does Carotid Occlusion Occur?
Carotid stenosis can occur due to factors such as atherosclerosis (arteriosclerosis). Risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes and overweight can cause plaque buildup on the artery walls. This can lead to thickening of the artery walls and blockage of the carotid artery.
What are the Symptoms of Carotid Artery Occlusion?
Carotid artery occlusion symptoms occur due to reduced or interrupted blood flow to the brain and face. These symptoms are as follows:
- Sudden weakness or paralysis in the face or one side of the body
- Speech difficulty or difficulty understanding
- Sudden loss of vision or changes in visual field
- Dizziness or instability
- Severe headache or migraine
These symptoms can occur suddenly and may require urgent medical attention.
How is It Diagnosed?
Carotid stenosis is usually diagnosed by a doctor's physical examination, the patient's symptoms, medical history and other tests. Tests used for diagnosis include ECG, blood tests, angiography and chest x-ray.
What are the Risk Factors for Carotid Artery Occlusion?
Risk factors for carotid artery occlusion include the following:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history
- Old age
- Stress
- High salt consumption
- Alcohol consumption
- Atherosclerosis
Who Has Carotid Artery Occlusion?
Carotid stenosis is more common in older men. However, women are also at risk. It is also more common in people with a sedentary lifestyle, excessive alcohol consumption and obese people.
What are the Treatment Methods for Carotid Artery Occlusion?
Treatment for carotid artery occlusion varies depending on the degree of occlusion, the severity of the symptoms and the patient's state of health. Treatment options are as follows:
- Medication: Medicines can be used to control blood pressure, cholesterol levels and blood clotting.
- Vascular opening procedure: The plaques causing the blockage can be removed by passing a catheter through the vessel or a stent can be placed in the area of the plaque.
- Surgical treatment If the blockage of the carotid artery occlusion is severe and other treatment methods are inadequate, surgical treatment may be necessary. This involves reopening the artery causing the blockage or bypass surgery.
- Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes may be recommended to control risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking and overweight. These include a healthy diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking and avoiding stress.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Carotid stenosis is a condition caused by narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries. These arteries are two of the main vessels that carry blood to the brain. Narrowing or blockage can prevent adequate blood flow to the brain. It can lead to serious consequences such as stroke or brain damage.
-
Yes, carotid artery blockage can cause pain. It can also cause symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances, speech disturbances, loss of facial sensation or numbness.
-
In some cases, stenting the carotid artery may be an option for the treatment of carotid artery stenosis. The stent is used to open the blockage and improve blood flow.
-
Carotid artery blockage can damage the heart. This is because the carotid artery is the main artery supplying the brain and eyes. If it is blocked, there is not enough blood flow to these organs. This can lead to serious consequences such as brain damage, stroke, blindness or heart attack.
-
After stenting, the vessel can become blocked again. It is therefore important to have regular check- ups after stenting and to detect possible complications early. In addition, preventive measures, such as lifestyle changes, can reduce the risk of re-clogging.