Carotid Artery Narrowing or Occlusion Treatment
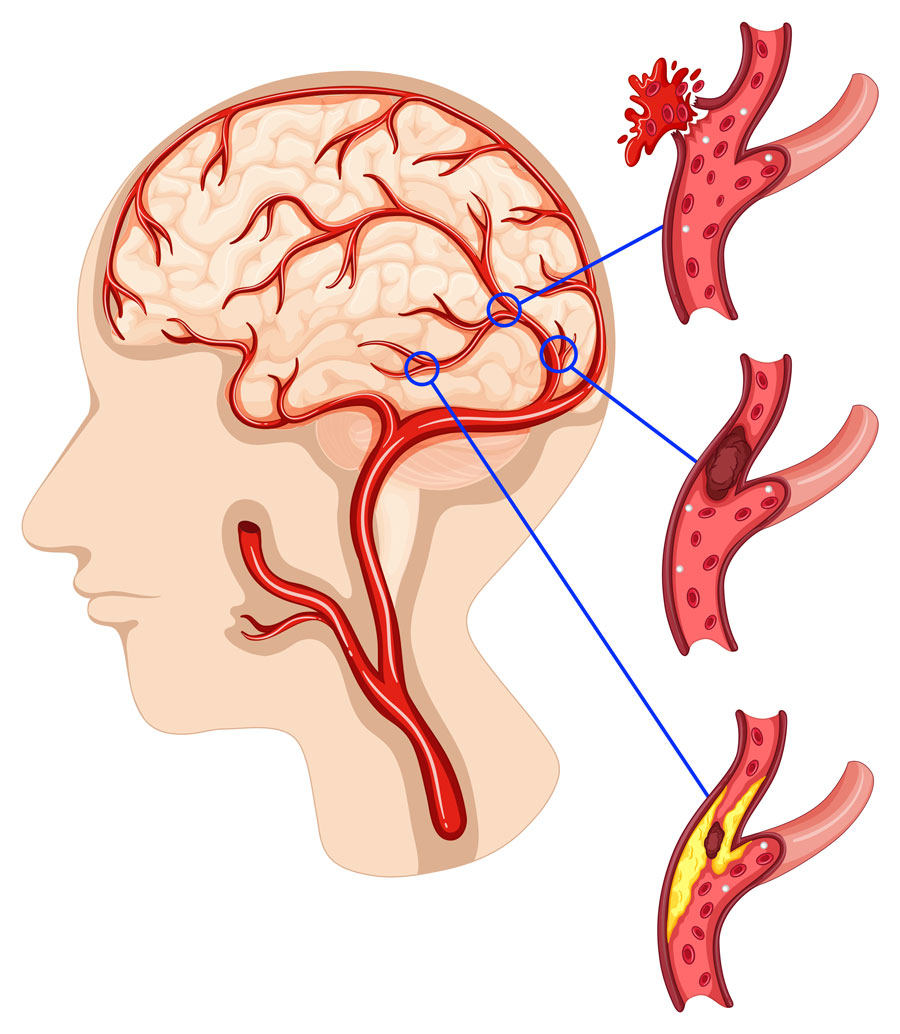
Carotid occlusion is caused by narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries in the neck. These arteries are one of the main vessels carrying blood to the brain. Therefore, due to blockage, the brain may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. This can lead to serious health problems such as stroke or paralysis. Carotid occlusion treatment aims to restore proper blood flow and prevent possible complications.
What Causes Carotid Narroeing or Occlusion?
Carotid artery occlusion occurs when the blood flow is reduced or completely stopped due to plaques or clots that form in the carotid arteries. The carotid arteries are one of the largest vessels carrying blood to the brain. For this reason, carotid occlusion can lead to insufficient blood flow to the brain and serious complications such as stroke. For this reason, carotid occlusion should be treated.
Who Has Carotid (Carotid artery) Occlusion?
Carotid occlusion usually occurs in old age. Other risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, diabetes and smoking.
How to Decide on Carotid Occlusion Treatment Process?
When deciding on a course of carotid occlusion treatment, factors such as the severity of the disease, symptoms, lifestyle and general health are taken into account. Doctors usually recommend that patients with carotid occlusion change their lifestyle. For example, patients should stop smoking, follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly and control other health problems such as blood pressure and cholesterol.
How is Carotid Artery Narrowing or Occlusion Treated?
If the symptoms and severity of carotid occlusion are above a certain level, the patient needs to be treated. Suitable options for the carotid occlusion treatment include medication, endovascular treatment and surgical intervention.
Drug therapy is used to help prevent blood clots and control blood pressure. Endovascular treatment is invasive procedures such as opening the blockage with a balloon and stent through a guide wire and catheter. Surgical intervention for carotid occlusion treatment is surgery to remove plaque in the area of the blockage or to clear the blockage.
What is the Stent Procedure and How Is It Performed?
A stent is a medical device used to open or widen a blocked or narrowed blood vessel. It is mostly used to treat blockages in the arteries of the heart. The procedure is a catheterization procedure performed by cardiologists. It is usually performed under local anesthesia.
The stent procedure is usually performed by making a small incision in the femoral artery or an artery in the arm. The cardiologist guides a catheter through the vessel and uses a fluoroscopy device to locate the blocked or narrowed vessel by transferring images to a screen. A catheter with a balloon is then placed over the blockage and the balloon is inflated to open the blockage. Finally, a small metal device called a stent is inserted into the vessel to keep the blockage open.
What are Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Congestion?
Lifestyle changes that should be made to prevent and treat carotid occlusion are as follows:
- A healthy diet (low fat, low salt and low cholesterol diet)
- Regular exercise
- Smoking cessation
- Stress management
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Stenting a blocked vessel depends on the rate of blockage. In general, stents are inserted in vessels that are 70 to 100 percent blocked. However, since each patient's condition is different, the doctor determines which blockage rate requires stenting.
-
Stent lifetime varies depending on many factors. But generally, the long-term effectiveness of the stent depends on factors such as material quality, stent location, patient lifestyle and other medical conditions. Some stents can last a lifetime, while others can last between 5 and 10 years.
-
An angioplasty procedure for the carotid occlusion treatment is performed by accessing an artery in the groin or arm area of the patient and using guide wires and catheters to locate the blockage and place a stent. The angioplasty procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia and may require an overnight hospital stay.
-
The carotid artery is a large artery that carries blood to the head and brain. If the carotid artery is completely blocked, this prevents sufficient blood flow to the brain. This deprives brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients.
-
A complete blockage of the carotid artery can cause serious brain damage. This is called carotid artery occlusion or carotid artery thrombosis. Carotid artery thrombosis can often lead to serious consequences such as stroke.
-
After stent placement, the patient may need to rest and restrict activities for a certain period of time in accordance with the doctor's advice. This usually takes 24 to 48 hours. The patient will be instructed by the doctor to gradually return to normal activities in the weeks following stent placement.
-
Patients should regularly take all medications prescribed by the doctor, including blood thinners and other medications after stenting. It is also important to improve blood circulation by leading a healthy lifestyle and exercising regularly.